The Importance of Aviation for Africa’s Development
Aviation is a crucial driver of economic growth, trade, and tourism in Africa. With a vast landmass and a significant number of landlocked countries, air travel is often the fastest and most efficient means of transportation. The airline industry facilitates business expansion, cross-border investments, and regional connectivity, helping African economies integrate into the global market. However, despite its importance, the sector faces significant challenges that hinder its full potential.
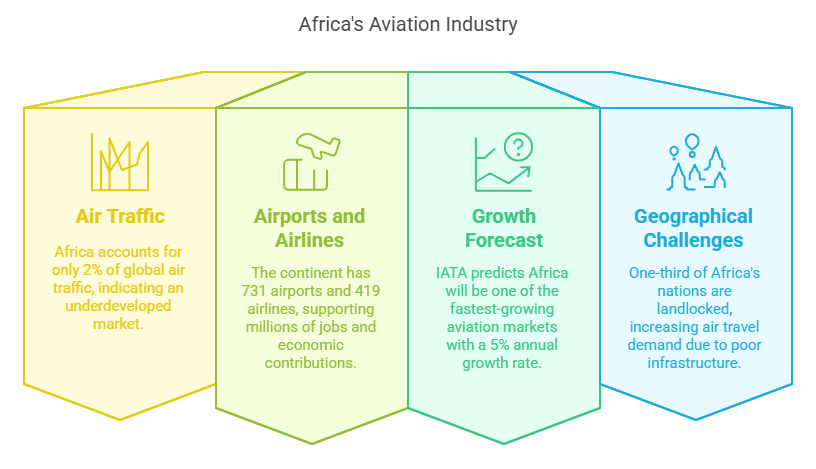
Africa’s Aviation Industry in Numbers
- Africa accounts for only 2% of global air traffic, reflecting its underdeveloped market compared to other regions.
- The continent has 731 airports and 419 airlines, supporting 6.9 million jobs and contributing $80 billion to the economy.
- The International Air Transport Association (IATA) forecasts that Africa will be among the fastest-growing aviation markets, with an estimated annual growth rate of 5% over the next 20 years.
- The geographical layout of Africa, with one-third of its nations being landlocked, increases the demand for air travel, especially in regions with poor road and rail infrastructure.
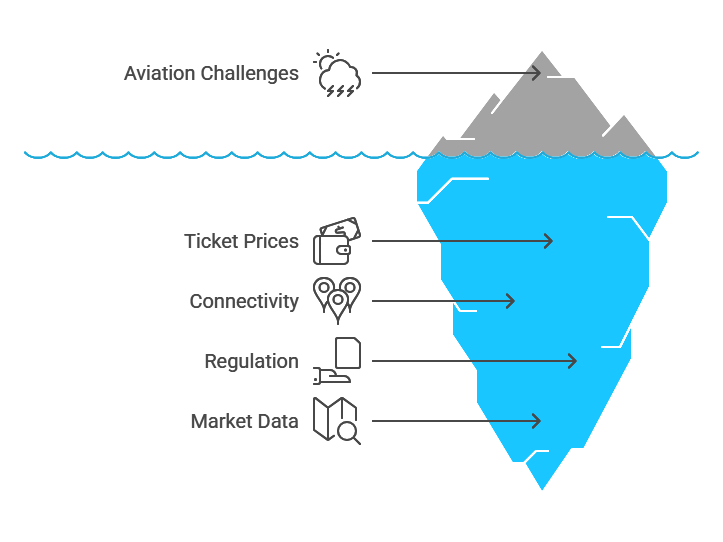
Key Challenges Facing Africa’s Aviation Sector
High Ticket Prices and Heavy Taxation
One of the biggest obstacles to aviation growth in Africa is the high cost of air travel. According to the BBC, Africa has some of the most expensive flight tickets in the world due to:
- Excessive airport taxes and fuel levies, which make up nearly 50% of ticket prices.
- High air navigation and landing fees, discouraging budget airlines and making travel unaffordable for many.
- Limited competition, allowing airlines to keep fares high.
Infrastructure Gaps and Limited Connectivity
Many African airports lack modern facilities, runways, and air traffic control systems, creating operational inefficiencies. Some key issues include:
- Underdeveloped regional hubs, leading to longer layovers and indirect routes.
- Insufficient investment in new airports and renovations, affecting flight frequency and capacity.
- Landlocked countries facing limited transport alternatives, making air travel essential but costly.
Regulatory Barriers and Market Restrictions
Unlike Europe or the US, where airspace is largely deregulated, African aviation is heavily controlled by bilateral air service agreements (BASAs). These restrictions result in:
- Limited competition, reducing affordability and connectivity.
- Slow implementation of the Yamoussoukro Decision (YD), which was meant to liberalize Africa’s air transport sector.
- Barriers to foreign investment in African airlines, preventing much-needed capital injections.
Lack of Market Data and Investment Challenges
The absence of comprehensive aviation analytics and market insights discourages investors from entering the African airline industry. This results in:
- Difficulty in identifying profitable routes and optimizing operations.
- A lack of confidence from private investors and international stakeholders.
- Minimal access to funding and expansion opportunities for new airlines.
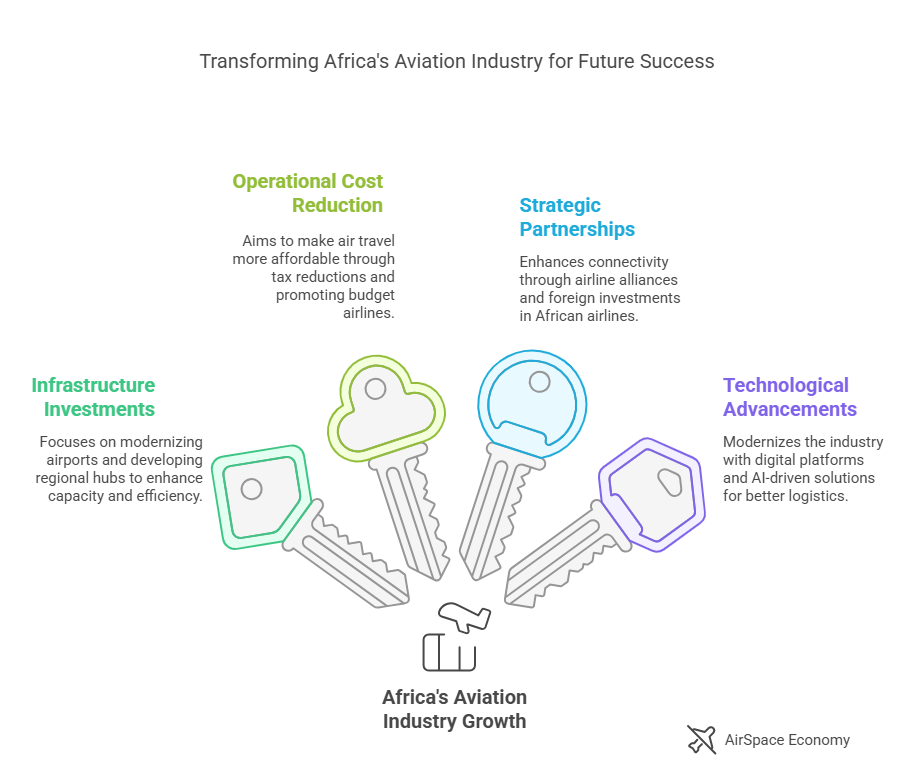
Opportunities for Growth in Africa’s Aviation Industry
Expanding Infrastructure and Investments
Africa’s aviation sector has huge investment potential, particularly in:
- Airport modernization projects, increasing passenger capacity and efficiency.
- Developing regional aviation hubs, reducing reliance on long layovers.
- Encouraging public-private partnerships (PPPs) to fund infrastructure upgrades.
Lowering Operational Costs and Improving Affordability
To make air travel more accessible, policymakers and industry leaders can:
- Reduce fuel taxes and airport levies, allowing airlines to lower ticket prices.
- Promote budget airlines, which have successfully expanded air travel in regions like Asia and Europe.
- Offer government incentives and tax breaks to airlines investing in African routes.
Strengthening Regional and International Partnerships
Strategic partnerships can enhance connectivity and industry competitiveness through:
- Interline agreements and airline alliances, allowing seamless transfers between African and global carriers.
- Foreign direct investment (FDI) in African airlines, fostering industry growth and operational improvements.
- Collaboration between governments and aviation stakeholders to improve regulations and encourage open skies policies.
Technology and Innovation in African Aviation
Technological advancements can modernize the African airline industry through:
- Digital booking and payment platforms, improving accessibility for passengers.
- AI-driven market analytics, enabling airlines to optimize pricing and route planning.
- Drone technology and alternative transport solutions, supporting cargo logistics in remote areas.
Africa’s aviation industry is at a pivotal moment—it has immense potential for growth, yet it remains constrained by high costs, regulatory barriers, and infrastructure deficits. By implementing open skies agreements, modernizing airports, lowering operational costs, and embracing technology, African aviation can thrive and become a key player in global air transport.
Collaboration between governments, private investors, and international stakeholders is essential to overcoming these barriers and unlocking Africa’s full aviation potential. With the right policies and investments, the future of African aviation is bright.







